Running Quality Assurance Reports
You can run quality assurance (QA) reports to review your translated projects for discrepancies between the source and target segments. This is a way to check the quality of your translations before sending your project for review, returning a translation to a client, or exporting the final, translated project. These reports can be useful because they can help find errors that you might not have otherwise noticed, such as formatting inaccuracies, repeated segments, or termbase errors. By running a QA report, you can locate errors and correct them early in the translation process, preventing unnecessary rework later.
How to Run Quality Assurance Reports
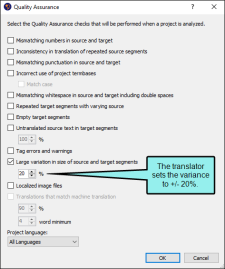
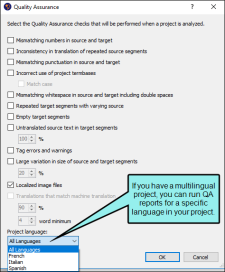
- Select File > Project QA. The Quality Assurance dialog opens.
-
Select the check boxes for the quality assurance reports you want to run.
-
Mismatching numbers in source and target This report shows segments where numerals are not the same in the source and target segments.
Example
Let's say you have a source segment that contains a reference to the year 1805. During translation, the translator mistypes in the target segment, and types a 7 instead of a 5.
When the translator runs the QA report to find mismatching numbers in the source and target segments, Lingo recognizes this error and identifies the segment where the mistake was made. The translator can then go back and fix the mistyped year.
-
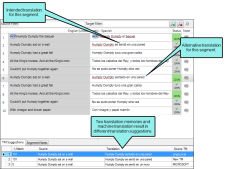
Inconsistency in translation of repeated source segments This report shows segments where two identical source segments do not have identical translations.
Example
Let's say you have two options in the translation memory for a particular segment. While translating, the translator selects the same translation almost every time. However, he occasionally selects the alternative translation. This results in inconsistent target segments.
When the translator runs the QA report to find inconsistent translation of repeated source segments, Lingo recognizes the error and identifies the segments where the incorrect segment was chosen. The translator can then go back and correct the translation so all identical source segments have consistent translations.
-
Mismatching punctuation in source and target This report shows segments where punctuation is missing or does not match between the source and target.
Example
Let's say you have a segment that does not have any punctuation at the end of it. However, the translator accidentally added a period at the end of the target segment when translating.
When the translator runs the QA report to check for mismatched punctuation, Lingo recognizes the error and identifies the segment where there is an incorrect period. The translator can then go back and fix the inaccurate punctuation.
-
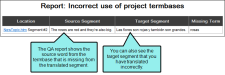
Incorrect use of project termbases This report reviews the termbase to find instances where a word is improperly used. Select the Match Case option if you want to limit results so the report only finds terms that match the casing saved in the termbase.
Example
Let's say your company uses termbases to define preferred definitions for words and phrases with multiple definitions. While translating, the translator manually translates a segment and uses an alternative term that does not match the termbase definition.
When the translator runs the QA report to locate incorrect uses of the project termbases, Lingo identifies locations where the termbase was incorrectly used. The translator can then go back and fix the incorrect word.
-
Mismatching whitespace in source and target including double spaces This report shows segments where spacing is inconsistent between the source and target segments.
Example
Let's say your translator is manually translating some source segments that are not in the translation memory. While typing, the translator types an extra space between two words, and it falls at a line break, so it is very difficult to identify.
When the translator runs the QA report to check for mismatching whitespace in the source and target segments, Lingo identifies the extra space between words that would otherwise have been difficult to see. The translator can then go back and remove the extra space.
-
Repeated target segments with varying source This report shows segments where identical target segments do not have the same source segment.
Example
Let's say your translator is manually translating a long list of segments. While translating, the translator inadvertently looks at another segment in the Translation Editor and retranslates that segment into the selected target segment.
When the translator runs the QA report to find repeated target segments with a varying source segment, Lingo recognizes the error and identifies the two identical target segments that should have different translations. The translator can then go back and fix the mistake.
-
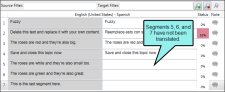
Empty target segments This report finds target segments that have not yet been translated.
Example
Let's say you have a very long project with many topics to translate. While translating, the translator intentionally leaves a few segments to translate later. After translating these segments, he wants to be sure that he didn't forget anything.
When the translator runs the QA report to find empty target segments, Lingo finds a few untranslated segments, and the translator can return to the topics to complete the translations.
-
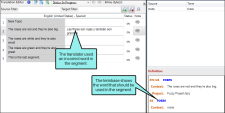
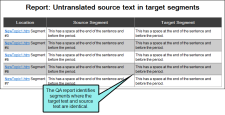
Untranslated source text in target segments This report shows segments where the source text appears in both the source and target segment. You can use the drop-down to set a threshold for the amount of text that appears in both segments.
Example
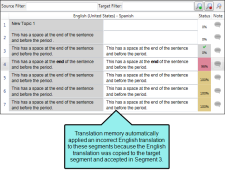
Let's say your translator is using the translation memory to translate the project's source segments. One of the segment's translation suggestions was incorrectly saved in the TM; its translation is the same as the English text in the source segment. When the translator applies the TM to the entire project, the English translation is applied to the segment it matches.
When the translator runs the QA report to find untranslated source text in target segments, Lingo identifies the segments where the target text and the source text are identical. The translator can then go back and correct the error.
Example
Let's say you have a project that has many words that do not have direct translations, such as names. If you set a low threshold for untranslated text, Lingo will pick up all of these items in the QA report.
In this report, the threshold is set at 10%. Because Lingo is picking up all of the untranslated names and showing these segments in the report, it is hard to find the one instance where the source was inadvertently copied to the target, about halfway down the report.
If you adjust the threshold higher, it is easier to see possible errors. Here, the threshold is set at 60%. You can still see names that match in the source and target segment, but you can also see where a segment was accidentally copied over to the target segment.
-
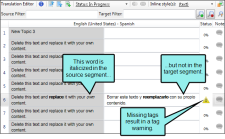
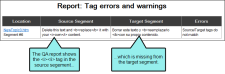
Tag errors and warnings This report shows segments where there is a tag error or warning because of a missing or open tag.
Example
Let's say you have a source segment with formatting throughout the segment. One word is bold and another is italic. While translating, the translator includes the formatting on the bold word, but does not format the italic word. As a result, a tag warning appears on the segment to indicate that there is a missing tag in the target segment.
When the translator runs the QA report to check for tag errors or warnings, Lingo identifies the segment where there is a missing tag. The translator can then go back and update the segment with the correct formatting.
-
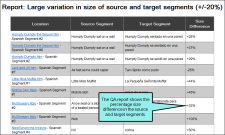
Large variation in size of source and target segments This report shows segments where either the source or target differ in length by more than the defined threshold.
Example
Some target languages use many more letters than English to spell a particular word, while some use many fewer. Let's say your target segments are consistently about 20% longer than the source segment. If they are much shorter or longer, it may indicate a translation error. In the Quality Assurance dialog, the translator sets the segment variance to +/- 20%.
When the translator runs the QA report to see large variations in the size of the source and target, she can see variations in the target segment that are at least 20% smaller or larger than the source segment. She can then review these segments for errors and correct any that may be mistakes.
-
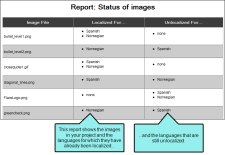
Localized image files This report shows the localization status of all of the images in your project. The report shows the languages for which you have chosen a new image ("localized" images), as well as those still using the original source file ("unlocalized" images).
Example
Let's say you are translating a project into 10 different languages. As part of the translation process, you need to localize all of the images in the project. During the course of your project, several new topics are added to the source project, and you receive new images that you need to localize.
Because there have been so many changes to the project, you periodically run the localized image files report to see the localization status of each image in the project. When you run the report, you can see each original image, what languages have been localized for each image, and what languages have not been localized for each image. This helps you keep track of which images you still need to update.
The following image shows how such a report might look.
-
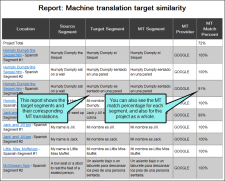
Translations that match machine translation This report compares the translated target segment with any available machine translations (MTs). This lets you review your translations against the machine translations and make changes if necessary. You can change the threshold for the minimum MT match percentage, and you can set a minimum number of words in the segment (to prevent obvious matches, such as names or short phrases, from appearing in the results).
Note This report is unavailable if an MT provider is not connected to the project.
Example
Let's say you regularly send your Lingo projects out for translation. You want to make sure that your translators are not relying too heavily on MT, because your company uses several company-specific terms that are located in your concordance and in your translation memories, but would not be found in a translation from an MT.
When you get your translations back from the translators, you run a QA report to see which translations match the MT. You set the percent match at 90% and the minimum word match to 4 words.
When you look at the report, you can see which translations are at least a 90% match to the MT. You may want to review these translations to make sure that your translators made the appropriate adjustments to the machine-generated translations.
-
-
(Optional) If you are working with a multilingual project, you can run reports for a specific language in your project. Select the language you want to use for the QA report from the Project language drop-down. You can select an individual language or all languages.
Note You will only see this option if you are working with a multilingual project.
-
Click OK. The QA report(s) open in a new tab.
Note If you filtered your project using target or condition filters, the reports reflect the filters you applied. You can only report on files that are part of your current project. See Dynamic Filtering.
- (Optional) You can print or save your report. In the local toolbar, click
 to print the report. Click
to print the report. Click  to save the report as an HTML file.
to save the report as an HTML file.