When creating a project in Lingo, you can use a filter to translate only specific content in a folder or in certain file types. Filters allow you to set restrictions on the content in a file or folder that is available for translation. Filters are available for Word, text, and XML files. They are also available for folders, so you can choose the file types in the folder that you want to translate.
Once you create a filter, you can save it to reuse it later, and you can apply it to all other files of the same type in the project.
Examples
This screenshot shows how to access a file type filter.
This screenshot shows how to access a folder filter.
When you create a Lingo project, you can create a project from a folder. You can filter the file types in the folder so only some files are included in the translation project. You can also create additional filters for any Word, XML, or text files that may be in the folder so only certain parts of the file are imported for translation. See Creating New Projects.
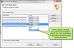
If you want to select the file types in the folder to import for translation, click the File Types link. The Translatable File Types dialog opens.
In the Translate column, select the file types you want to import. You can click the Select All check box to add all the file types at once.
If you want to create file type filters for the files within the folder, select Customize Folder from the Filter drop-down. The File Types Filters dialog opens.
If you want to filter the translated files, you can create a file type filter. Use the Filter drop-down to select an existing filter, or select Create New to create a new one. You can add file type filters to XML, Word, or text files.
When creating a new project in Lingo, you can add files to your project in the Start a New Project Wizard. If you want to filter the translated files, you can create a file type filter. Use the Filter drop-down to select an existing filter, or select Create New to create a new one. You can add file type filters to XML, Word, or text files. See Creating New Projects.
From the Filter drop-down, select Create New.
Enter a name for your filter and click OK. The File Filters dialog opens.
 .
.Delete a Filter Select a filter from the Filter drop-down, then click  .
.
Note: If you delete a filter, it will be removed from all translation projects where it is currently in use.
Insert tag Select this option to keep soft breaks or tabs together with the rest of the segment. Lingo adds a tag where the soft break or tab appears in the segment.
Example
The two segments pictured below include a soft break and a tab, respectively. The Word file type filter in Lingo has been set to add a tag when there is a tab or a soft break, but it will not split the segment. When translating the segment, you can drag the tag into the target segment where it needs to appear.
Insert tag and create new segment Select this option to create a new segment wherever there is a soft break or a tab in your project.
Example
The two segments pictured below include a soft break and a tab, respectively. The Word file type filter in Lingo has been set to add a tag when there is a tab or a soft break, and it will also create a new segment at the location where the tab or soft break appears. When translating the segment, you can drag the tag into the target segment where it needs to appear.
Include hidden text Select this option to include hidden text in the Lingo project so it can be translated.
Example
The segment below includes hidden text. Lingo places a tag where the hidden text appears in the original Word document, so the location of the text is clearly visible in the Translation Editor. However, in this example, the Lingo file type filter is set so hidden text is not included for translation. When translating the segment, you can drag the tag into the target segment where it needs to appear.
In the segment below, the filter has been changed so hidden text is included. Notice that the word "HIDDEN" is now visible. Lingo also places a tag on either side of the hidden text so the text is clearly visible in the Translation Editor. You can drag the yellow tags onto the target segment to mark the hidden text in the target segment.
Include comments Select this option to include comments as separate segments in the Lingo project so they can be translated. If you do not select this option, comments will not be included.
Example
The segment below includes a comment. Lingo places a tag on either side of the phrase that was marked with a comment in the original Word document, so the location of the comment is clearly visible in the Translation Editor. However, in this example, the Lingo file type filter is set so the comment itself is not included for translation.
In the segment below, the filter has been changed so the comment itself is included. Notice that the comment is visible in a second segment. This allows you to translate the comment separately. You can also still see the comment tag in the first segment that indicates where the comment was marked in the original Word document. When translating the sentence, you can drag the yellow tag onto the phrase that needs the comment in the target segment. Later, when you export the document, the comment will appear in the finished project, attached to the appropriate location in the document.
Include index Select this option to include index entries as separate line items in the Lingo project so they can be translated. If you do not select this option, index entries will not be included.
Example
The segment below includes words that are marked as index entries. Lingo places a tag next to the text that was marked with a keyword in the original Word document, so the location of the index keywords are clearly visible in the Translation Editor. When translating the segment, you can drag the tag into the target segment where it needs to appear. However, in this example, the Lingo file type filter is set so the index entry itself is not included for translation.
In the segment below, the filter has been changed so the index entries itself are included. Notice that each word in the index is visible, so three additional segments follow the original segment. This allows you to translate each index entry separately. You can also still see the keyword tags in the first segment that indicates where the keywords were marked in the original Word document.
Include footnotes/endnotes Select this option to include footnotes or endnotes as separate segments in the Lingo project so they can be translated. If you do not select this option, footnotes or endnotes will not be included.
Example
The segment below includes a footnote. Lingo places a tag next to the sentence that was marked with a footnote in the original Word document, so the location of the footnote is clearly visible in the Translation Editor. When translating the segment, you can drag the tag into the target segment where it needs to appear. However, in this example, the Lingo file type filter is set so the footnote itself is not included for translation.
In the segment below, the filter has been changed so the footnote is included as a separate segment. This allows you to translate the footnote separately. You can also still see the footnote tag in the first segment that indicates where the footnote was marked in the original Word document.
In the Styles/Markup area, select the check box if you want to include minor formatting changes in your translation project.
Example
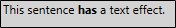
The segment below includes a text effect, and also includes bold formatting. However, in this example, the Lingo file type filter is set so the text effect is not visible in Lingo. You can only see the bold formatting.
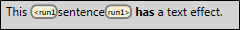
In the segment below, the filter has been changed so the text effect is visible. Lingo places a tag next to the word that was marked with a text effect in the original Word document, so the location of the effect is clearly visible in the Translation Editor. When translating the sentence, you can drag the yellow tag onto the word that needs the text effect in the target segment. Later, when you export the document, the text effect will appear in the finished project.
When creating a new project in Lingo, you can add files to your project in the Start a New Project Wizard. If you want to filter the translated files, you can create a file type filter. Use the Filter drop-down to select an existing filter, or select Create New to create a new one. You can add file type filters to XML, Word, or text files. See Creating New Projects.
From the Filter drop-down, select Create New.
 .
.Delete a Filter Select a filter from the Filter drop-down, then click  .
.
Note: If you delete a filter, it will be removed from all translation projects where it is currently in use.
(Optional) If you want to associate a DTD or XML schema with the XML file, click  . In the dialog that opens, locate the schema or DTD file you want to use, then click Open.
. In the dialog that opens, locate the schema or DTD file you want to use, then click Open.
In the Candidate Tags section, select the tags from XML file that you want to translate. If a tag can be translated, it will be checked in the Translatable column. If you do not want to translate a tag, remove the checkmark from this column.
Example
You might want to translate tags that are words, but tags that consist of all numbers might not be good candidates for translation. You should remove the checkmark from the Translatable column for these tags.
 to add the tag. If you want to remove a tag, select it from the list, then click
to add the tag. If you want to remove a tag, select it from the list, then click  .
.In the Candidate Attributes section, select the attributes from XML file that you want to translate.
Note: If a tag does not have any attributes, nothing displays in this section. If you do not see any attributes in the Candidate Attributes section, try selecting a different tag.
 to add the attribute. If you want to remove an attribute, select it from the list, then click
to add the attribute. If you want to remove an attribute, select it from the list, then click  .
.(Optional) When you are adding a filter to an XML file, you can place restrictions on the attributes in the file to tell Lingo when to include or exclude an element for translation. You can also remove restrictions if you no longer need them.
Click Restriction. The Attribute Restriction dialog opens.
Select the restriction you want to apply. You can include or exclude the element if the attribute value is listed.
In the Add Attribute Value field, enter any additional attribute values you want to add. These tags do not need to be in the XML file at this time, but if you know that they may be in the file in the future, you can add them here. Enter the name for the attribute value, then click  to add the value. If you want to remove a value, select it from the list, then click
to add the value. If you want to remove a value, select it from the list, then click  .
.
Click OK. The restriction appears in the File Filters dialog.
In the Candidate Attributes area of the File Filters dialog, select the attribute with a restriction.
Click Restriction. The Attribute Restriction dialog opens.
When creating a new project in Lingo, you can add files to your project in the Start a New Project Wizard. If you want to filter the translated files, you can create a file type filter. Use the Filter drop-down to select an existing filter, or select Create New to create a new one. You can add file type filters to XML, Word, or text files. See Creating New Projects.
From the Filter drop-down, select Create New.
 .
.Delete a Filter Select a filter from the Filter drop-down, then click  .
.
Note: If you delete a filter, it will be removed from all translation projects where it is currently in use.
In the Segment field, enter a regular expression to identify the text you want to translate.
In the Note field, enter a regular expression to identify the text you want to include as a note for each segment.
Example
Let's say you have a text file that looks like this:
You want to include everything on the left side of the text file (between the quotation marks) as a note in your translatable file, and everything on the right side of the text file (after the equal sign) as the segment for translation.
To accomplish this, you would create a filter using regular expressions that look like this:
When you create the project, it will look like this:
You can edit a file filter after you apply it to a project. When you update the project, the new filter settings will be applied.