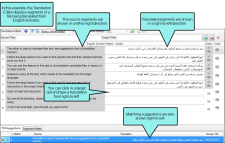
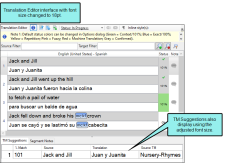
Translation Editor
This editor is used to translate files and use suggestions from a translation memory (TM) database and/or a machine translation (MT) service.
Text from left-to-right (LTR) languages is aligned left, and columns holding right-to-left (RTL) text is aligned right, allowing you to type in the correct direction.
For certain types of files (e.g., Microsoft Word documents; PowerPoint files; Flare topics, snippets, template pages) the Translation Editor lets you work in Translation (or grid) mode and open Live Preview mode as well. When you want to translate text, you use the Translation mode, which displays source text segments in a column on the left and target text segments in a column on the right. When you want to view your translations in their intended context (in complete paragraphs, with formatting, etc.), you can click a button in the local toolbar to switch to Live Preview mode, where you can continue to translate text in the left pane and while looking at a preview of your changes in the right pane.
[Menu Proxy — Headings — Online — Depth3 ]
How to Open This Editor
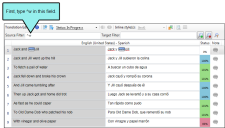
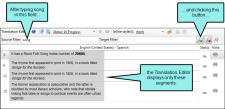
- Open the File List window pane (View > File List).
- (Optional) By default files are displayed in a grid. If instead you want to view them in a folder structure, click
 in the local toolbar. Clicking this button a second time switches you back to grid view.
in the local toolbar. Clicking this button a second time switches you back to grid view. - (Optional—if using the grid view) Next to the Filter field at the top of the window pane, you can click the down arrow and select one of the options to limit the file types shown (e.g., snippets). If you are new to Lingo, you may want to select "All Files" to view all of the translatable files in your project.
- Double-click any file in the list.
Local Toolbar
Use the buttons in the bar at the top of the editor to perform actions in either Translation mode or Preview mode.
|
|
Hides or shows special information pertaining to the editor or window pane. |
|
|
Uploads the selected segment to translation memory. |
|
|
Uploads all segments in the file to translation memory. |
|
|
Lets you select the status for the open file. Alternatively, you can open the Properties dialog for the file (via the File List window pane) if you want to set the same status for multiple files. |
|
|
Splits the segment where the cursor is placed in the source cell so that it becomes two segments. |
|
|
Joins two or more selected segments so that they become one segment. In order to join segments they must be part of the same translation unit (e.g., same paragraph, same list item). If you select segments that are not part of the same translation unit, the join option is disabled. |
|
|
Turns space markers on and off. When you turn this feature on, you can see markers that show where space exists between text in a segment. |
|
|
Lets you select and apply inline formatting such as bold, italic, or underlined to text in the target cell. This field is enabled only if the source segment contains that formatting somewhere. |
|
|
Applies 100% and 101% matching suggestions from TM to the appropriate segments in the file. |
|
|
Toggles between the Live Preview mode and the Translation mode of the editor. This button is displayed only for certain types of files. |

|
Toggles the location of the Live Preview pane to display to the right of the Translation Editor or below the Translation Editor. This button is enabled only when using Live Preview mode. |
|
|
This button displays if you have an image file open. Clicking this button opens a dialog that lets you select a different background image for the open file. |
Filter Fields
Use the fields and buttons above the grid to perform searches to temporarily reduce the number of segments shown in the grid below.
|
Source Filter |
Enter text that you want to find in the source segments. |
|
Target Filter |
Enter text that you want to find in the target segments. |
|
|
Initiates the search. |
|
|
Clears the filter fields and returns the grid to its original state. |
|
|
Lets you select options to perform a search with regular expressions or to be case-sensitive. |
Example
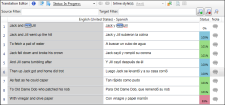
Let's say you have the following segments in the Translation Editor:
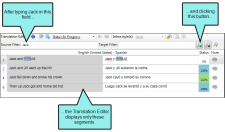
You want to limit the segments shown to only those where the name "Jack" appears in the source segments. So you type Jack in the Source Filter field and click  . As a result, only a few segments are now shown.
. As a result, only a few segments are now shown.
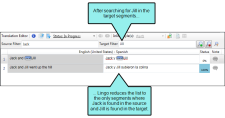
Then let's say you want to further limit the segments so that, of those shown, only those with "Jill" on the target side are included. Therefore, you type Jill in the Target Filter field and click  . Now the list of segments is further reduced.
. Now the list of segments is further reduced.
Example — Regular Expression
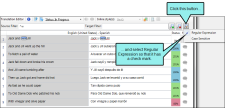
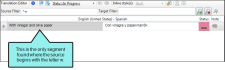
Let's say you want to limit the results to only segments where the source sentences begins with the letter w. First, you enter ^w in the Source Filter field. This is a regular expression that looks for lines that begin with w.
Then you click  and select Regular Expression. This enables Lingo to use the expression you just typed.
and select Regular Expression. This enables Lingo to use the expression you just typed.
Finally, you press ENTER on your keyboard and the list is shortened.
Example — Case-Sensitive
Let's say you have the following segments in the Translation Editor:
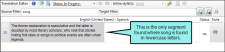
You want to limit the segments shown to only those that contain the word "song" in the source. So you type song in the Source Filter field and click  . As a result, only a few segments are now shown.
. As a result, only a few segments are now shown.
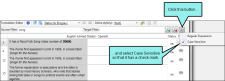
However, let's say you want to limit the results to only the segments where the word is lowercase. So you click  and select Case Sensitive.
and select Case Sensitive.
After you click  again, only one segment is found where song is found in lowercase.
again, only one segment is found where song is found in lowercase.
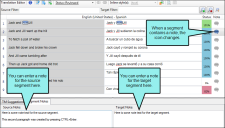
Translation Mode
Translation (or grid) mode lets you work with the file content in text strings organized in columns. As the name suggests, this is the mode you will use when actually translating content.
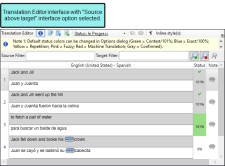
On the Interface tab of the Lingo Options dialog (File > Options), you can customize the way the Translation Editor and Translation Memory Editor display translation segments. You can display the source and target segments next to each other, or with the source segment above the target segment. You can also adjust the editor font size, which resizes translation segments, translation suggestions, and segment notes based on your desired font size.
Main Interface Elements
|
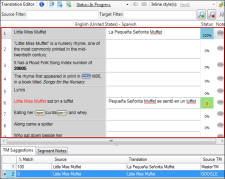
[Source Language] |
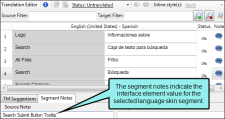
Displays the text in the source language. Note Skin files from Flare projects are already translated into various languages. Therefore, most of the time you will not see segments from a skin file displayed in the Translation Editor. However, if the author makes a change to a text string in the original Flare project, that segment will be displayed in the Translation Editor. |
|
[Target Language] |
You can type translation text in these cells. Then press ENTER on your keyboard to confirm the translation. |
|
Status |
Displays a background color and TM match percentage for each segment. |
|
Note |
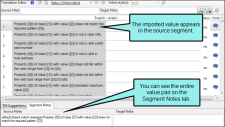
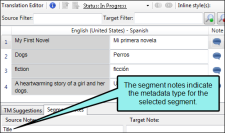
Displays an icon to indicate the presence of a note for the segment. For example, you might want to add a note to remind yourself to do additional research about a term, or to tell a reviewer why a particular translation was used. If the icon is gray, no note exists. If the icon is colored, a note exists. When you click on the icon, the Segment Notes tab at the bottom of the editor displays so that you can see or enter any notes for the source or target segment. If you want to create a new paragraph, press CTRL+ENTER. After you enter a note, the icon changes in the Note column. Note When translating .properties files, only the value is translatable. The entire value pair is added to the segment as a segment note for your reference. Note You can translate metadata tags in PDF and EPUB targets. The metadata type is added to the segment as a segment note for your reference. Note When translating language skin segments, the interface element value is added to the segment as a segment note for your reference. Note Segment notes travel with the project. Therefore, if you create a new Lingo project based on the same source files, the same notes will not automatically be associated with those segments because it is a new project. Note When you import a review package from Contributor, any annotations from the reviewer are added to the segment as segment notes. |
|
TM Suggestions |
If you are using translation memory (TM), any matching translations are displayed in this tab at the bottom of the editor. If you want to use an existing match, double-click it and then press ENTER on your keyboard to confirm the translation for the segment. This area also shows suggestions from machine translation (MT) services. |
|
Segment Notes |
Use this tab to enter source or target notes for a segment. |
Right-Click Menu
|
Cut |
Cuts the selection and sends it to the clipboard. |
|
Copy |
Copies the selection and sends it to the clipboard. |
|
Paste |
Pastes the selection from the clipboard to the place where the cursor is inserted. |
|
Confirm |
Confirms the translation, adds it to TM (if applicable), and moves focus to the next segment. You can also press ENTER on your keyboard to do this. |
|
Split Segment |
Breaks the segment at the point where the cursor is placed, so that the one segment becomes two. |
|
Join Segments |
Merges the selected segments into a single segment. |
|
Add Note |
Opens the Segment Notes tab at the bottom of the Translation Editor. This lets you type a note related to the selected segment (for the source and/or the target). When you are done, the Note icon to the right of the segment changes to reflect the fact that a note exists. |
|
Clear Target Segment |
Removes all content from the target cell. |
|
Copy Source to Target |
Copies all of the text, as well as the formatting or tags, from the source to the target cell. |
|
Add Next Tag |
Copies each tag in order from the source to the target cell. |
|
Add Next Number |
Adds each number in order from the source to the target cell. |
|
Add New Term |
Lets you add a term in the segment to a termbase. |
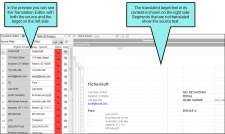
Live Preview Mode
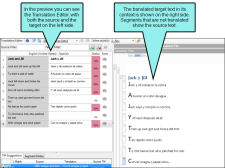
The Live Preview mode can be used for certain types of files and displays two window panes. The Translation Editor—with both the source and target segments—is shown in the left pane, and a preview of the document in the translated language is shown in the right pane. The Live Preview mode displays the file in the same way that the author edits it in the source tool (e.g., Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, Flare, Contributor), with content shown in complete headings, paragraphs, lists, and so on. When viewing the document in Live Preview mode, you can make changes in the Translation Editor pane, and they will display in real time in the Live Preview pane.
|
Translation Editor |
This is the left window pane, which displays the source and target segments for the file. You can make changes to the target segments in this pane, and changes will display in the live preview pane. |
|
Live Preview |
This is the right window pane, which displays the translated file in the target language. |
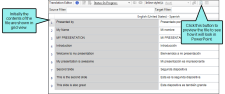
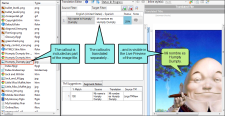
Example — Word
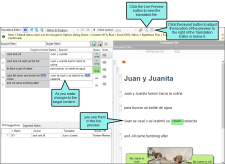
When you first open a Word file in Lingo, it may look something like this, with text segments in a grid.
After you click  , the file looks just like it would in Word. You can still see the Translation Editor and make changes, which appear in the preview area as you make them.
, the file looks just like it would in Word. You can still see the Translation Editor and make changes, which appear in the preview area as you make them.
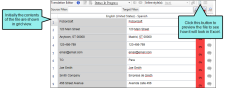
Example — Excel
When you first open an Excel file in Lingo, it may look something like this, with text segments in a grid.
After you click  , the file looks just like it would in Excel. You can still see the Translation Editor and make changes, which appear in the preview area as you make them.
, the file looks just like it would in Excel. You can still see the Translation Editor and make changes, which appear in the preview area as you make them.
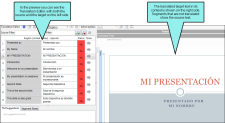
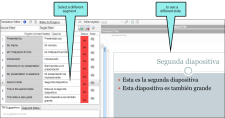
Example — PowerPoint
When you first open a PowerPoint file in Lingo, it may look something like this, with text segments in a grid.
After you click  , the file looks just like it would in PowerPoint. You can still see the Translation Editor and make changes, which appear in the preview area as you make them.
, the file looks just like it would in PowerPoint. You can still see the Translation Editor and make changes, which appear in the preview area as you make them.
If the PowerPoint document has multiple pages, and most do, select a different segment in the Translation Editor to view the slide.
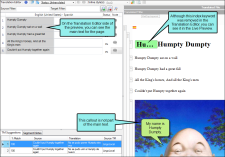
Example — Flare Project With Capture Image Callouts
This is an example of an untranslated Flare project, viewed in Live Preview mode. Notice that the callout is part of the preview. This is because the callout is part of the image, not part of the text for the topic file.
When you open the image file, you can translate the callout separately.
Note The Word preview feature supports DOC and DOCX files.
Note The PowerPoint preview feature supports only PPTX files, not PPT files.
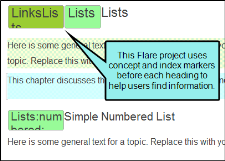
Note If you are looking at Flare or Contributor files, you might notice light green or dark green rectangles in the topic with text inside. These are index keywords and concepts, which are not translated in the same file. For example, if you want to translate all index keywords, you would open the Index.liindexmap file from the File List window pane.
Note If a concept or index tag appears at the beginning or end of a segment, it is not displayed in the Translation Editor. This makes segments look cleaner in the Translation Editor, and prevents translators from needing to move tags that are not related to the segment. Additionally, these tags are not displayed in Live Preview mode. Index and concept keywords are still displayed if they appear between two words. You can translate any index and concept tags in a project when you open the index keyword or concept keyword file from the File List window pane.